AI in Cybersecurity: How Machine Learning is Preventing Data Breaches
- Shilpi Mondal

- May 2, 2025
- 3 min read
SHILPI MONDAL|DATE:JANUARY 13 ,2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming cybersecurity by enhancing threat detection, automating responses, and preventing data breaches. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, traditional security measures often fall short, necessitating advanced solutions that can adapt and respond in real-time.
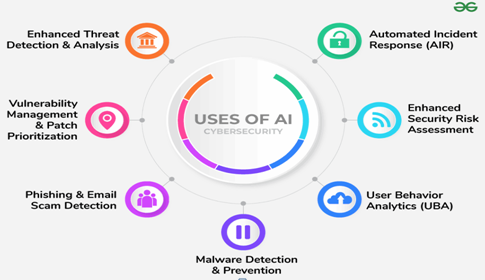
Enhancing Threat Detection
Machine learning algorithms sift through massive volumes of data to detect patterns indicative of criminal activities. By continuously learning from new data, these systems can spot anomalies and potential attacks that would otherwise go undetected by traditional security methods. For instance, ML can monitor network behavior to spot unusual access patterns, signaling a potential intrusion. AI can also automatically search networks and systems for vulnerabilities, making it easier to find possible points of entry for intruders.

Automating Incident Response
AI-driven cybersecurity solutions simplify regular processes, allowing security personnel to focus on more challenging concerns.These systems can swiftly identify, contain, and remediate breaches, reducing the time attackers have to exploit vulnerabilities. Automation is crucial for continuous monitoring, streamlined patch management, and efficient incident response. AI can be used, for instance, to read source code, analyze logs, anticipate attacks, find vulnerabilities, and even develop or exploit them.

Preventing Data Breaches
AI enhances data breach prevention through several key capabilities:
Predictive Analysis:
Anticipating possible risks using historical data and current patterns.
Real-Time Monitoring:
Real-time monitoring is the process of identifying and addressing hazards as they arise.
User Behavior Analytics:
Identifying deviations from typical user behavior that may indicate compromised accounts. UEBA systems collect data on typical user and entity activities within a network, establishing a baseline of normal behavior. By continuously monitoring and analyzing deviations from this baseline, UEBA can detect unusual behaviors that may indicate potential security threats, such as insider attacks or compromised devices.
Organizations can proactively patch vulnerabilities before they can be exploited because to these capabilities.

Challenges and Considerations
While AI provides enormous benefits, it also poses challenges:
Data Dependency:
In order to operate efficiently, AI systems need huge datasets, which raises questions around data security and privacy. The security difficulties associated with AI are similar to those encountered with prior generations of software that were not built with security in mind.
Adversarial Attacks:
Attackers may attempt to deceive AI systems by feeding them misleading dataML algorithms can be vulnerable to adversarial assaults, in which attackers intentionally modify input data to trick the system into producing incorrect predictions.
Resource Intensive:
Implementing AI solutions can be costly and require substantial computational resources. The barriers to adopting AI in cybersecurity include technical challenges in data integration and reliability concerns, as well as ethical and privacy concerns due to potential AI algorithms and data collection biases.
Future Outlook
The integration of AI in cybersecurity is expected to deepen, with advancements in machine learning models enhancing predictive capabilities and response times. Organizations are increasingly adopting AI-driven tools to stay ahead of cyber threats, recognizing the need for dynamic and adaptive security measures. AI has consistently demonstrated its potential as a tool for improved analysis, speed, and scale in cybersecurity applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI and machine learning are pivotal in modern cybersecurity strategies, offering tools to detect, prevent, and respond to data breaches more effectively than ever before. As technology evolves, so too will the methods to safeguard digital assets, with AI at the forefront of this ongoing battle against cyber threats.
Citations:
Akitra. (2023, December 19). Five latest applications of AI in cybersecurity - Akitra - Medium. Medium. https://medium.com/%40akitrablog/five-latest-applications-of-ai-in-cybersecurity-5efacd566691
Balbix Inc. (2024, October 21). Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity | Balbix. Balbix. https://www.balbix.com/insights/artificial-intelligence-in-cybersecurity/
Malik, K. (2024, December 16). AI in Cybersecurity: Benefits and Challenges. Astra Security. https://www.getastra.com/blog/ai-security/ai-in-cybersecurity/
What are the barriers to AI adoption in cybersecurity? (n.d.). Palo Alto Networks. https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/cyberpedia/what-are-barriers-to-ai-adoption-in-cybersecurity
R Street Institute. (2024, January 26). The Transformative Role of AI in Cybersecurity: Understanding Current applications and benefits - R Street Institute.
Image Citations:
GeeksforGeeks. (2024, June 3). AI in Cybersecurity Uses, Benefits and Challenges. GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ai-in-cybersecurity/
Ahmed, U., Nazir, M., Sarwar, A., Ali, T., Aggoune, E. M., Shahzad, T., & Khan, M. A. (2025). Signature-based intrusion detection using machine learning and deep learning approaches empowered with fuzzy clustering. Scientific Reports, 15(1).
Mktg, S., & Mktg, S. (2024, November 22). AI in Cybersecurity: Incident Response Automation Opportunities. SISA.
https://www.sisainfosec.com/blogs/incident-response-automation/
How to Prevent data Breaches in 2025 (Highly Effective Strategy) | UpGuard. (n.d.). https://www.upguard.com/blog/prevent-data-breaches




Comments